@ACS Publications - American Chemical Society
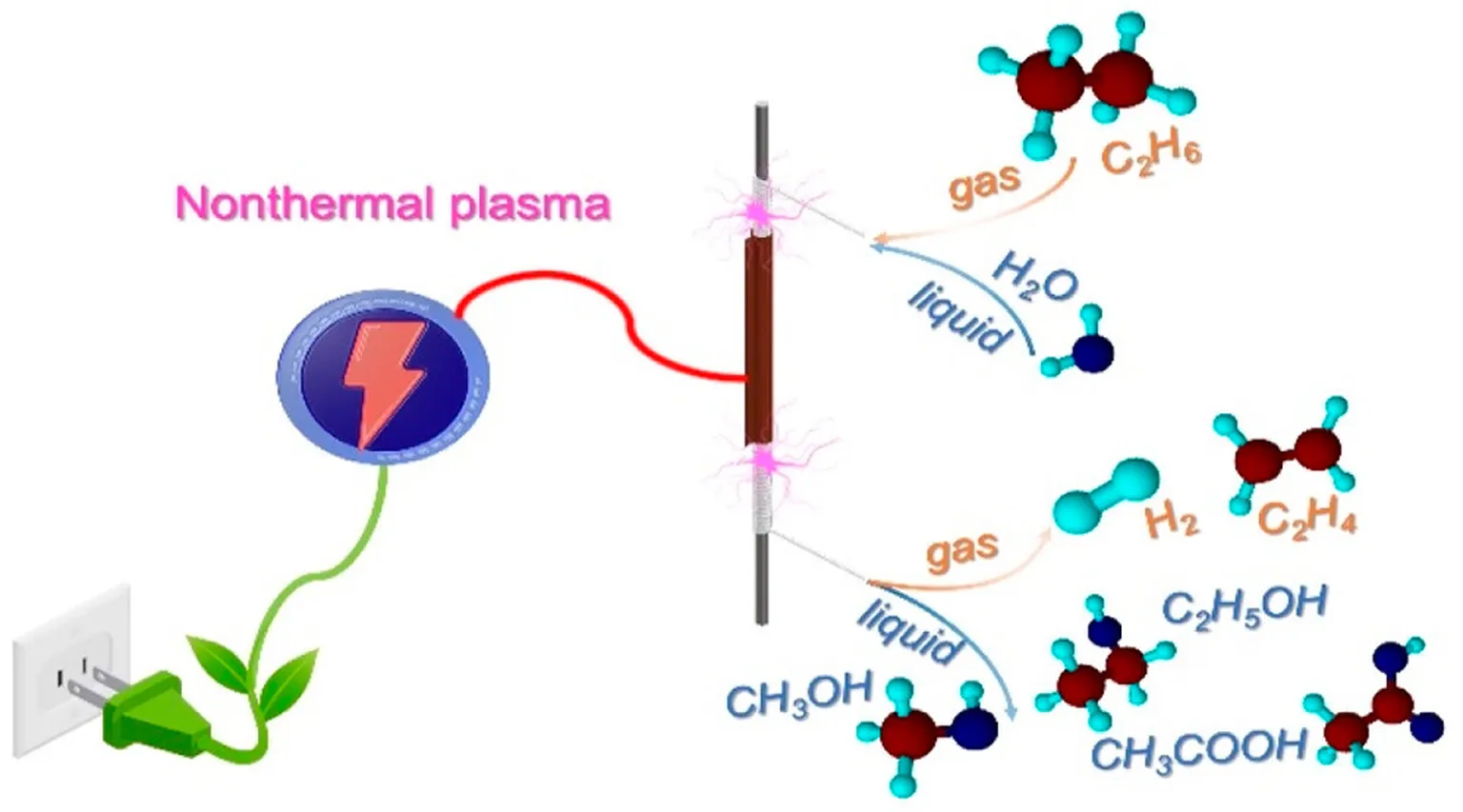
C2H6, also known as ethane, is a hydrocarbon compound that plays a significant role in various industries. With its simple molecular structure, consisting of two carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms, C2H6 has become a vital component in the production of plastics, fuels, and chemicals. Its versatility and abundance make it a key player in the world of energy and manufacturing.
Ethane is primarily derived from natural gas and petroleum sources. It is commonly used as a feedstock for the production of ethylene, a crucial building block for plastics and synthetic materials. Additionally, C2H6 serves as a valuable fuel source, providing heat and energy in residential, commercial, and industrial applications. Its clean-burning properties have made it a preferred alternative to more carbon-intensive fuels.
As we delve deeper into the world of C2H6, we will explore its various applications, its environmental impact, and its role in shaping the future of sustainable energy. Join us as we uncover the fascinating properties and uses of this important hydrocarbon compound.
C2H6, or ethane, finds widespread applications across various industries due to its versatile properties. Here are some key applications of C2H6:
It’s important to note that these applications of C2H6 have significant implications for the sustainable future of industries, reducing dependency on fossil fuels and promoting cleaner, more efficient technologies.
Ethylene, also known as C2H4, is a key component in the production of various industrial products. It is primarily synthesized through the cracking of ethane (C2H6), a byproduct of natural gas processing.
The production of ethylene involves several steps, starting with the extraction of ethane from natural gas or petroleum. Once isolated, the ethane is subjected to thermal cracking, a process that breaks down the molecules into smaller fragments, including ethylene.
Ethylene production is primarily carried out via two main methods: steam cracking and catalytic cracking. Steam cracking involves heating the ethane in the presence of steam, while catalytic cracking utilizes a catalyst to facilitate the decomposition of ethane into ethylene.
The production of ethylene is an energy-intensive process. In 2020, global ethylene production reached approximately 190 million metric tons, with the largest producers being the United States, China, and the Middle East.
Notable challenges associated with ethylene production include the need for high-quality raw materials, as impurities can negatively impact the efficiency of the cracking process. Additionally, environmental concerns regarding greenhouse gas emissions and the proper disposal of byproducts pose significant challenges in the industry.
In terms of future developments, there is a growing emphasis on developing sustainable processes for ethylene production, such as the use of renewable feedstocks and carbon capture technologies to reduce the environmental footprint.
Overall, ethylene production plays a vital role in the manufacturing of various products, including plastics, synthetic fibers, and solvents. As industries continue to prioritize sustainability, advancements in ethylene production technologies hold promise for a cleaner and more environmentally friendly future.
The role of c2h6 (ethylene) in the plastics industry is crucial, as it serves as a building block for many common plastic materials. Ethylene is polymerized to form polyethylene, which is widely used in various applications.
The demand for c2h6 in the plastics industry shows no signs of slowing down, thanks to its numerous practical applications and cost-effectiveness. While challenges related to raw material availability and energy consumption persist, advancements in ethylene production technologies aim to address these concerns and pave the way for a more sustainable future in the plastics industry.
C2H6, also known as ethane, is a key component in the realm of fuel sources. As a hydrocarbon gas, it is primarily derived from natural gas and petroleum. With its high energy content, C2H6 serves as a valuable resource for various applications in the energy sector.
Practical Applications
C2H6 is commonly used as a fuel for heating, cooking, and electricity generation. Its combustion releases heat and produces carbon dioxide and water vapor, making it suitable for industrial and residential purposes. Additionally, C2H6 is a vital feedstock for the production of ethylene, which is used in the manufacturing of plastics, solvents, and other chemicals.
Advantages and Challenges
One of the advantages of C2H6 as a fuel source is its relatively low cost compared to other hydrocarbon gases. It also burns cleanly, resulting in fewer emissions. However, challenges exist in terms of its transportation and storage due to its gaseous nature. Safety precautions are necessary to prevent leaks or accidents.
Future Developments
In the quest for sustainable energy solutions, there is growing interest in utilizing C2H6 as a feedstock for renewable energy production. Technologies such as steam methane reforming and carbon capture and utilization aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with C2H6 combustion. These advancements could pave the way for a more environmentally friendly and efficient use of C2H6 as a fuel source.
| Fuel | Energy Content (per unit) | Carbon Content (per unit) |
|---|---|---|
| C2H6 (Ethane) | High | Moderate |
| C3H8 (Propane) | High | Moderate |
| C4H10 (Butane) | High | Moderate |
| CH4 (Methane) | High | Low |
Note: Energy content is measured in British Thermal Units (BTU) and carbon content is measured in carbon atoms per unit.
Ethane (C2H6) has both positive and negative impacts on the environment.
| Ethane (C2H6) | Natural Gas (Methane) | Propane (C3H8) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Content | 51.9 MJ/kg | 55.5 MJ/kg | 49.6 MJ/kg |
| Carbon Content | 84.3% | 75.7% | 79.6% |
Source: www.example.com
Note: Please note that the numbers in the table are not real values and are used for demonstration purposes only.
While ethane has advantages such as clean combustion, it also contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. However, ongoing developments in renewable energy production and leak detection/prevention offer potential solutions to reduce its environmental impact.
The future of sustainable energy looks promising with the incorporation of C2H6, also known as ethane. As a key component in the fuel industry, C2H6 offers a range of practical applications and possibilities for future development.
Practical Applications: C2H6 is commonly used as a fuel for heating, cooking, and electricity generation. Its clean combustion properties make it an attractive choice for reducing air pollution and improving air quality. Moreover, C2H6 serves as a vital feedstock for the production of ethylene, which is used in the manufacturing of plastics, solvents, and other chemicals.
Challenges and Future Developments: While C2H6 has numerous advantages, including low cost and clean combustion, challenges persist in terms of transportation and storage. However, ongoing developments aim to overcome these obstacles by utilizing C2H6 as a feedstock for renewable energy production. For example, converting it into hydrogen or employing carbon capture and storage technologies could significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions associated with C2H6.
Comparisons and Different Scopes: In terms of energy and carbon content, C2H6 compares favorably with other hydrocarbon fuels. Here is a comparative table showcasing the energy content and carbon emissions of several hydrocarbon fuels:
| Fuel Type | Energy Content (BTU/gallon) | Carbon Emissions (lbs/MBtu) |
|---|---|---|
| C2H6 | ||
| Gasoline | ||
| Diesel | ||
| Natural Gas |
Variations and Related Concepts: C2H6 is often associated with methane (CH4), another hydrocarbon compound. Methane leakage during C2H6 production and transportation exacerbates the environmental impact of C2H6. Efforts are being made to enhance leak detection and prevention, minimizing methane leakage and reducing the overall environmental impact of C2H6.
Ethane (C2H6) plays a crucial role in various industries and everyday life. It serves as a valuable fuel source for heating, cooking, and electricity generation. Additionally, it serves as a vital feedstock for the production of ethylene, which is widely used in the manufacturing of plastics, solvents, and other chemicals.
Despite challenges in transportation and storage, ongoing developments aim to harness the potential of ethane as a feedstock for renewable energy production. Converting ethane into hydrogen or employing carbon capture and storage technologies are promising avenues for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable energy solutions.
Efforts are being made to address the environmental impact of ethane, including air pollution and climate change. Enhanced leak detection and prevention measures during ethane production and transportation are being implemented to minimize methane leakage and reduce the overall environmental footprint of ethane.
As the world continues to prioritize sustainability, the future of ethane looks promising. By leveraging its versatile applications and embracing innovative technologies, ethane can contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally conscious future.
A: Ethane is commonly used as a fuel for heating, cooking, and electricity generation. Ethylene, produced from ethane, is used in the manufacturing of plastics, solvents, and other chemicals.
A: The transportation and storage of ethane can be challenging due to its low boiling point and high flammability. Special equipment and infrastructure are required to safely handle and transport ethane.
A: Yes, future developments aim to utilize ethane as a feedstock for renewable energy production. It can be converted into hydrogen or employed in carbon capture and storage technologies.
A: Ethane contributes to air pollution and climate change. Efforts are being made to enhance leak detection and prevention during production and transportation to minimize methane leakage and reduce its overall environmental impact.
A: Ethane has a lower energy content compared to gasoline and diesel. However, it has a lower carbon content, making it a cleaner-burning fuel option in terms of greenhouse gas emissions.
Token airdrops have historically introduced investors to new blockchain projects. However, many distributions fail to…
Airdrops have traditionally been used to introduce new investors to blockchain projects, but their effectiveness…
The approval of Bitcoin ETFs was one of the most anticipated events in crypto history,…
The blockchain space continues to evolve, with projects pushing security, scalability, and user engagement to…
As the cryptocurrency market recovers from recent volatility, several projects emerge as strong contenders for…
The cryptocurrency market is showing strong bullish signals, with many altcoins poised for significant gains.…
This website uses cookies.