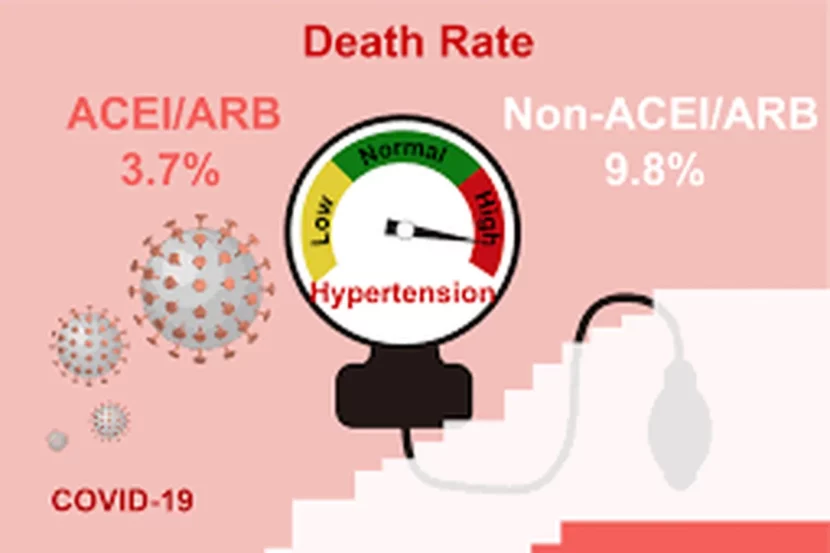
ARB drugs, also known as Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers, have become a crucial component in the treatment of various cardiovascular conditions. These medications work by blocking the action of a hormone called angiotensin II, which can cause blood vessels to constrict and increase blood pressure. By inhibiting this hormone, ARB drugs help relax blood vessels and lower blood pressure, making them an effective choice for managing hypertension and heart failure.
Not only do ARB drugs help control blood pressure, but they also offer additional benefits for patients with certain medical conditions. For instance, these medications have been found to be particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes, as they can help protect the kidneys and reduce the risk of diabetic nephropathy. Furthermore, ARB drugs have shown promise in preventing strokes and improving outcomes in patients with heart disease.
With their ability to effectively manage blood pressure and provide additional protective effects, ARB drugs have become an essential tool in the fight against cardiovascular diseases. In the following article, we will explore the mechanisms of action, potential side effects, and the role of these medications in various medical conditions. So, let’s dive deeper into the world of ARB drugs and discover their impact on cardiovascular health.
Mechanisms of Action of ARB Drugs
ARB drugs, or Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers, work by blocking the action of the hormone angiotensin II. By doing so, they help relax blood vessels and lower blood pressure. This is achieved by binding to and blocking the angiotensin II receptors, preventing the hormone from constricting blood vessels and increasing blood pressure.
When angiotensin II is blocked, the blood vessels are allowed to dilate, leading to improved blood flow and reduced strain on the heart. This makes ARB drugs effective in managing hypertension and heart failure.
Another mechanism of action for ARB drugs is their ability to protect the kidneys in patients with diabetes. By blocking angiotensin II, they help reduce the risk of diabetic nephropathy, a leading cause of kidney damage in diabetic patients.
In addition to their cardiovascular benefits, ARB drugs have shown promise in preventing strokes and improving outcomes in patients with heart disease. By inhibiting angiotensin II, they help reduce the risk of blood clot formation and improve blood circulation to the brain and heart.
Overall, the mechanisms of action of ARB drugs involve blocking the hormone angiotensin II, leading to relaxation of blood vessels, lower blood pressure, improved kidney function, and reduced risk of stroke and heart disease complications.
Benefits of ARB Drugs for Hypertension and Heart Failure
ARB drugs have shown significant benefits in the management of hypertension and heart failure. These medications work by blocking the hormone angiotensin II, which helps relax blood vessels and lower blood pressure. By allowing blood vessels to dilate and reducing strain on the heart, ARB drugs effectively lower blood pressure and improve heart function.
Here are some key benefits of ARB drugs for hypertension and heart failure:
• Blood pressure control: ARB drugs help reduce blood pressure by blocking the action of angiotensin II, a hormone that constricts blood vessels. This leads to improved blood flow and decreased pressure on the walls of the arteries.
• Heart failure management: ARB drugs are also effective in the management of heart failure. They help the heart pump blood more efficiently by reducing the strain on the heart muscle and improving its overall function.
• Reduction in cardiovascular events: Studies have shown that ARB drugs can reduce the risk of cardiovascular events, such as heart attacks and strokes, in patients with hypertension and heart failure. These medications improve blood circulation and reduce the risk of blood clot formation.
• Kidney protection: In addition to their benefits in hypertension and heart failure, ARB drugs are also beneficial in protecting the kidneys, especially in patients with diabetes. They help reduce the risk of diabetic nephropathy, a condition that can lead to kidney damage.
ARB drugs provide multiple benefits in the management of hypertension and heart failure. They help control blood pressure, improve heart function, reduce the risk of cardiovascular events, and protect the kidneys. These medications play a crucial role in improving cardiovascular health and overall well-being.
Role of ARB Drugs in Diabetes Management
Core Principles: ARB drugs, or angiotensin receptor blockers, are commonly used to manage diabetes. They work by blocking the action of a hormone called angiotensin II, which constricts blood vessels and raises blood pressure. By blocking this hormone, ARB drugs help to lower blood pressure and improve blood flow to the kidneys.
Key Components: ARB drugs target the angiotensin II type 1 receptors in the body. By blocking these receptors, they prevent angiotensin II from binding to them and exerting its effects. This leads to dilation of blood vessels and reduced blood pressure.
Operation within Diabetes Management: ARB drugs have several important roles in the management of diabetes. They help to lower blood pressure, which is essential in preventing and managing complications such as diabetic nephropathy and cardiovascular diseases. ARB drugs also have a renoprotective effect, meaning they help protect the kidneys from damage caused by diabetes.
Types and Categories: There are several ARB drugs available on the market, including losartan, valsartan, and candesartan. Each of these drugs has slight variations in their chemical structure, but they all work in a similar way to block the angiotensin II receptors.
Practical Applications: ARB drugs are commonly used in diabetic patients with hypertension or proteinuria. They are effective in lowering blood pressure and reducing the risk of kidney damage. These medications also have the potential to slow the progression of diabetic retinopathy, a complication that affects the eyes.
Challenges and Future Developments: While ARB drugs are generally well-tolerated, they may have side effects such as dizziness, fatigue, and cough. Ongoing research aims to develop more specific ARB drugs with fewer side effects and even better efficacy in managing diabetes.
Related Concepts: ACE inhibitors, another class of medications used in diabetes management, have a similar mechanism of action to ARB drugs. Both classes of drugs target the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and help lower blood pressure. However, ACE inhibitors work by blocking the enzyme that converts angiotensin I to angiotensin II, while ARB drugs specifically block the angiotensin II receptors.
Preventing Strokes with ARB Drugs
Preventing Strokes with ARB Drugs
ARB drugs play a crucial role in preventing strokes, a common complication of diabetes. These medications, such as losartan and valsartan, work by blocking the hormone angiotensin II, which constricts blood vessels and raises blood pressure.
By inhibiting angiotensin II, ARB drugs help to lower blood pressure, reduce the risk of stroke, and improve blood flow to the brain. They are particularly effective in patients with high blood pressure or those who have already experienced a stroke.
Studies have shown that ARB drugs can significantly reduce the risk of stroke in individuals with diabetes. A meta-analysis of clinical trials involving ARB drugs demonstrated a 20% reduction in the incidence of stroke compared to placebo.
It is important to note that ARB drugs are just one component of a comprehensive diabetes management plan. Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and controlling blood sugar levels, are also essential in reducing the risk of stroke and other diabetes-related complications.
In the future, ongoing research aims to develop more specific ARB drugs with fewer side effects. These advancements may further improve the stroke-preventing abilities of ARB drugs, offering new options for individuals with diabetes.
To learn more about preventing strokes with ARB drugs, check out this link for additional information.
Improving Outcomes in Heart Disease with ARB Drugs
ARB drugs play a crucial role in improving outcomes for individuals with heart disease. These drugs, also known as angiotensin receptor blockers, work by blocking the hormone angiotensin II, which constricts blood vessels and raises blood pressure. By inhibiting this hormone, ARB drugs help to lower blood pressure, reduce the risk of stroke, and improve blood flow to the heart.
Key points:
- ARB drugs lower blood pressure and improve blood flow to the heart.
- By blocking angiotensin II, these drugs reduce the risk of stroke in individuals with heart disease.
- ARB drugs are a key component of a comprehensive heart disease management plan.
Practical applications:
- ARB drugs are commonly prescribed to individuals with hypertension and heart failure.
- They are used in combination with other medications to manage high blood pressure and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events, such as stroke.
- ARB drugs are also beneficial for individuals who cannot tolerate other types of blood pressure medications, such as ACE inhibitors.
Challenges:
- Side effects, such as dizziness, fatigue, and cough, can occur with ARB drug use.
- Compliance with medication regimens can be a challenge, leading to suboptimal outcomes.
- Ongoing research aims to develop more specific ARB drugs with fewer side effects to further improve their effectiveness and tolerability.
- Ongoing research is exploring the potential of combining ARB drugs with other medications, such as statins, to further improve cardiovascular outcomes.
- The development of personalized medicine may lead to more targeted use of ARB drugs based on individual patient characteristics and genetic factors.
- New formulations and delivery methods, such as extended-release formulations and implantable devices, may enhance the effectiveness and convenience of ARB drug therapy.
[Link to external reference or source]
| ARB Drugs | Other Blood Pressure Medications | |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism of Action | Block angiotensin II receptors | Act on different pathways |
| Key Benefits | Lower blood pressure, reduce risk of stroke | Reduce blood pressure, prevent heart attacks |
| Common Side Effects | Dizziness, fatigue, cough | Cough, dizziness, rash |
| Dosage Forms | Tablets, capsules, oral solutions |
Conclusion
ARB drugs play a crucial role in managing heart disease by blocking the hormone angiotensin II. By doing so, they effectively lower blood pressure, reduce the risk of stroke, and improve blood flow to the heart. These drugs are commonly prescribed to individuals with hypertension and heart failure, often in combination with other medications, to effectively manage high blood pressure and minimize the risk of cardiovascular events.
Although there can be side effects and challenges associated with ARB drug use, ongoing research aims to develop more specific ARB drugs with fewer side effects. Additionally, exploring potential combinations with other medications and advancements in personalized medicine and new formulations may further enhance the effectiveness and convenience of ARB drug therapy.
Overall, ARB drugs provide significant benefits in improving outcomes for individuals with heart disease. With ongoing research and advancements in drug development, the future looks promising for enhancing the effectiveness and safety of ARB drug therapy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are ARB drugs?
ARB (angiotensin II receptor blocker) drugs work by blocking the hormone angiotensin II, which constricts blood vessels and raises blood pressure.
How do ARB drugs improve outcomes for individuals with heart disease?
By inhibiting angiotensin II, ARB drugs help to lower blood pressure, reduce the risk of stroke, and improve blood flow to the heart.
Who are ARB drugs commonly prescribed to?
ARB drugs are commonly prescribed to individuals with hypertension and heart failure.
Are there any side effects of ARB drug use?
Yes, side effects of ARB drug use can include dizziness and fatigue.
What are the challenges with ARB drug use?
Challenges with ARB drug use can include compliance with medication regimens.
What ongoing research is being conducted on ARB drugs?
Ongoing research aims to develop more specific ARB drugs with fewer side effects, explore potential combinations with other medications, and enhance the effectiveness and convenience of ARB drug therapy.